In the smart control center project at the Shijiu Port area of Rizhao Port, Holtop's advanced heat recovery system, renowned for its exceptional energy-saving capabilities, has played a key role in helping Rizhao Port meet its ambitious target of creating passive ultra-low-energy buildings.

Rizhao Port is leading the evolution in port construction, transitioning from labor-intensive to technology-intensive practices. The new control center, once completed, will establish an integrated platform for comprehensive control, management, and intelligent scheduling of production processes across the entire southern region. Leveraging advanced technologies such as AI, machine vision, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the center aims to facilitate automated and unmanned operations, thereby significantly improving efficiency and safety.
The construction requirements for this project were demanding. The office building spans 11 floors, and from the earliest planning stages, the goal was clear: to create a passive ultra-low-energy consumption building. This aspiration heavily influenced the design of the air conditioning system, leading to the adoption of a passive design strategy aimed at balancing comfort and energy efficiency. After weighing numerous alternatives, an air conditioning heating recovery fresh air unit system, based on Holtop's rotary heat recovery air conditioning units, was selected. Collaborative efforts led to the successful implementation of energy-saving measures.

Passive ultra-low energy buildings adapt to climatic characteristics and natural conditions, offering a comfortable indoor environment through superior thermal insulation and airtightness, fresh air heat recovery technology, and the use of renewable energy. These buildings not only provide a comfortable indoor environment but also contribute to energy conservation, which holds significant implications for the sustainable development of our society.
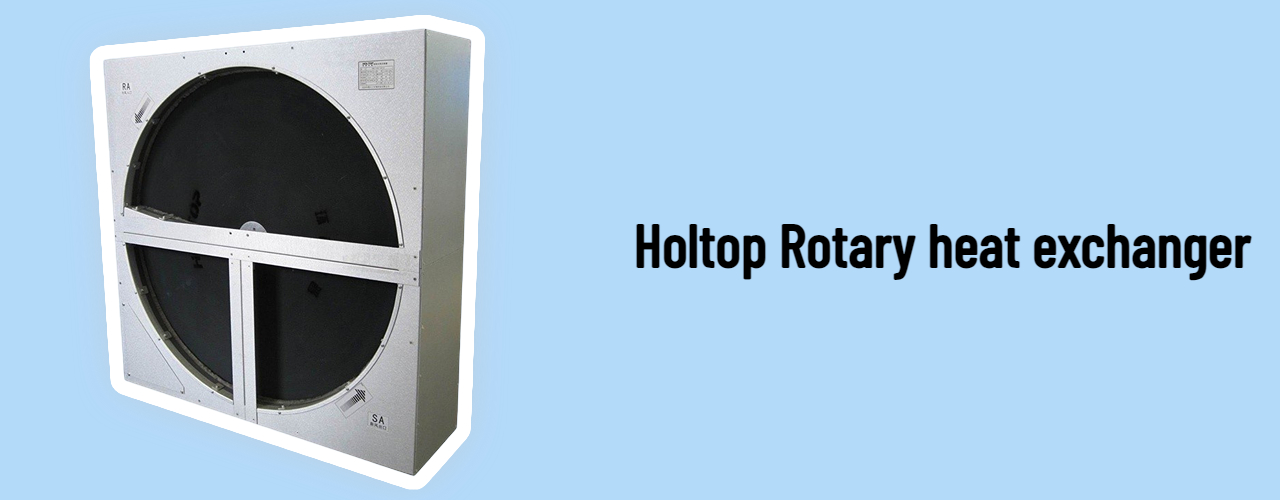
The control center demands a substantial volume of fresh air, around 40,000 volumes per hour. Multiple rotary heat recovery units have been deployed to deliver fresh air to the different floors. The advantages of the rotary heat exchanger shine in large air volume heat recovery systems. The rotary heat exchanger consists of a rotating wheel that carries supply and exhaust air. The wheel rotates 14 times per minute, with one half dedicated to supply air and the other to exhaust air. This configuration allows energy from the exhaust air to be transferred to the fresh air, thus enabling energy recovery. Given its compact size and high heat recovery efficiency, the rotary wheel is ideally suited for large air volume fresh air units.
After extensive discussions, site inspections, and scientific selection software calculations, Holtop finalized the heat recovery unit solution. For example, during summer, the exhaust air temperature is roughly 25 degrees Celsius. Discharging this air would be wasteful. Instead, the system brings in outdoor air at 35 degrees Celsius into the indoor environment, which would otherwise require continuous cooling by the air conditioning system. With Holtop's rotary heat recovery air conditioning units, the heat from the exhaust air is recovered via the rotary wheel. This allows the indoor supply air temperature to reach 27.5 degrees Celsius, with a heat recovery efficiency of over 75%, significantly reducing the load on the air conditioning system. This heat recovery technology successfully reconciles the need for comfort and energy efficiency in air conditioning, thus becoming a hallmark of energy efficiency in the control center building at Rizhao Port.

Holtop remains dedicated to the research and development of air heat recovery technology, aimed at reducing energy consumption of air conditioning systems by leveraging various core components of heat exchangers. These components are widely used across numerous types of buildings, such as residential, commercial, and office buildings, large venues, hospitals, and factories. Holtop continues to strive to be a pioneer in energy-saving and emission reduction initiatives.
Post time: Jun-26-2023